用友u8显示互斥任务申请不成功(u8互斥如何解决)
日期:2023年04月28日 09:05 浏览量:1
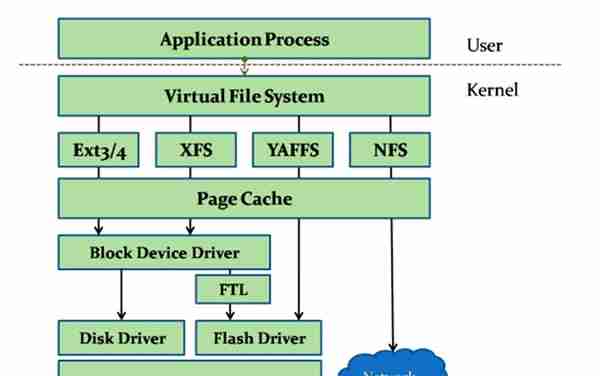
虚拟文件系统VFS
VFS的作用就是采用标准的系统调用读写位于不同物理介质上的不同文件系统。VFS是一个可以让open()、read()、write()等系统调用不用关心底层的存储介质和文件系统类型就可以工作的粘合层。在古老的DOS操作系统中,要访问本地文件系统之外的文件系统需要使用特殊的工具才能进行。而在Linux下,通过VFS,一个抽象的通用访问接口屏蔽了底层文件系统和物理介质的差异性。每一种类型的文件系统代码都隐藏了实现的细节。因此,对于VFS层和内核的其它部分而言,每一种类型的文件系统看起来都是一样的。
现在先了解一下VFS的数据结构:虽然不同文件系统类型的物理结构不同,但是虚拟文件系统定义了一套统一的数据结构:超级快对象、索引节点对象、 目录项对象、文件对象。
1.超级块对象
超级块对象代表一个具体的已安装文件系统,一般是一个分区有一个超级块。各种文件系统都必须实现超级块对象,该对象存储文件系统的信息,使用struct super_block结构体表示,在include/linux/fs.h文件中
struct super_block {
struct list_head s_list; //超级快链表头,指向所有超级块
dev_t s_dev; //设备号
unsigned char s_blocksize_bits;//块大小,单位为位
unsigned long s_blocksize;//块大小,单位为字节
loff_t s_maxbytes;//文件大小上限
struct file_system_type *s_type;//文件系统类型
const struct super_operations *s_op;//超级块操作方法函数
const struct dquot_operations *dq_op;//磁盘限额方法函数
const struct quotactl_ops *s_qcop;//限额控制方法函数
const struct export_operations *s_export_op;//导出方法函数
unsigned long s_flags;//挂载标志位
unsigned long s_iflags;//
unsigned long s_magic;//文件系统的魔数,每种文件系统类型被分配一个唯一的魔幻数
struct dentry *s_root;//目录挂载点
struct rw_semaphore s_umount;//卸载信号量
int s_count;//超级块引用计数
atomic_t s_active;//活动引用计数
#ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY
void *s_security;//指向安全模块
#endif
const struct xattr_handler **s_xattr;//扩展的属性
#if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_FS_ENCRYPTION)
const struct fscrypt_operations *s_cop;//文件加密方法函数
#endif
struct hlist_bl_head s_roots; /* alternate root dentries for NFS */
struct list_head s_mounts; /* list of mounts; _not_ for fs use */
struct block_device *s_bdev;//相关的块设备
struct backing_dev_info *s_bdi;
struct mtd_info *s_mtd;//存储磁盘信息
//把同一个文件系统类型的所有超级块实例链接在一起,链表的头节点是结构体file_system_type的成员fs_supers
struct hlist_node s_instances;
unsigned int s_quota_types; /* Bitmask of supported quota types */
struct quota_info s_dquot;//磁盘配额相关选项
struct sb_writers s_writers;//超级块使用信息
char s_id[32];//超级块名字,也是分区名字
uuid_t s_uuid; /* UUID */
void *s_fs_info;//文件系统私有信息
unsigned int s_max_links;//文件链接上限
fmode_t s_mode;//安装权限
/* Granularity of c/m/atime in ns.
Cannot be worse than a second */
u32 s_time_gran;//文件访问修改时间的最小单位
/*
* The next field is for VFS *only*. No filesystems have any business
* even looking at it. You had been warned.
*/
struct mutex s_vfs_rename_mutex; /* Kludge */
/*
* Filesystem subtype. If non-empty the filesystem type field
* in /proc/mounts will be "type.subtype"
*/
char *s_subtype;//文件系统子类型
const struct dentry_operations *s_d_op; //默认的超级块中目录操作方法函数
/*
* Saved pool identifier for cleancache (-1 means none)
*/
int cleancache_poolid;//保存池标识符
......
/*
* Owning user namespace and default context in which to
* interpret filesystem uids, gids, quotas, device nodes,
* xattrs and security labels.
*/
struct user_namespace *s_user_ns;//拥有者
/*
* Keep the lru lists last in the structure so they always sit on their
* own individual cachelines.
*/
struct list_lru s_dentry_lru ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp;//最近最少使用的目录链表
struct list_lru s_inode_lru ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp;//最近最少使用的文件链表
struct rcu_head rcu;
struct work_struct destroy_work;
struct mutex s_sync_lock; /* sync serialisation lock */
/*
* Indicates how deep in a filesystem stack this SB is
*/
int s_stack_depth;//指示此超级块在文件系统堆栈中的深度
/* s_inode_list_lock protects s_inodes */
spinlock_t s_inode_list_lock ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp;//超级块锁
struct list_head s_inodes;//超级块中所有文件的链表
spinlock_t s_inode_wblist_lock;//回写需要的锁
struct list_head s_inodes_wb;//需要回写的文件链表
} __randomize_layout;
超级块对象中最重要的是成员是const struct super_operations *s_op;这是超级块操作方法函数:
struct super_operations {
struct inode *(*alloc_inode)(struct super_block *sb);//创建和初始化一个新的索引节点
void (*destroy_inode)(struct inode *);//释放一个索引节点
void (*dirty_inode) (struct inode *, int flags);//处理脏索引节点的函数,日志文件系统通过此函数进行日志更新
int (*write_inode) (struct inode *, struct writeback_control *wbc);//将制定的索引节点写入磁盘
int (*drop_inode) (struct inode *);//索引节点引用计数为0时执行此函数
void (*evict_inode) (struct inode *);//删除磁盘的索引节点,硬链接计数为0时会执行此函数
void (*put_super) (struct super_block *);//释放超级块,卸载文件系统时调用
int (*sync_fs)(struct super_block *sb, int wait);//使文件系统和磁盘数据同步
int (*freeze_super) (struct super_block *);//锁定超级块
int (*freeze_fs) (struct super_block *);//做快照以前调用,阻塞更新,文件系统处于一个一致的状态
int (*thaw_super) (struct super_block *);//超级块解锁
int (*unfreeze_fs) (struct super_block *);//做完快照调用,可以继续更新文件系统
int (*statfs) (struct dentry *, struct kstatfs *);//读取文件系统的统计信息
int (*remount_fs) (struct super_block *, int *, char *);//重新挂载文件系统
void (*umount_begin) (struct super_block *);//卸载文件系统
int (*show_options)(struct seq_file *, struct dentry *);//查看文件系统装载的选项,用于proc文件系统
int (*show_devname)(struct seq_file *, struct dentry *);//查看硬件设备名称
int (*show_path)(struct seq_file *, struct dentry *);//查看挂载路径
int (*show_stats)(struct seq_file *, struct dentry *);//查看文件系统的统计信息,用于proc文件系统
#ifdef CONFIG_QUOTA
//磁盘限额使用功能函数
ssize_t (*quota_read)(struct super_block *, int, char *, size_t, loff_t);
ssize_t (*quota_write)(struct super_block *, int, const char *, size_t, loff_t);
struct dquot **(*get_dquots)(struct inode *);
#endif
int (*bdev_try_to_free_page)(struct super_block*, struct page*, gfp_t);
long (*nr_cached_objects)(struct super_block *,
struct shrink_control *);
long (*free_cached_objects)(struct super_block *,
struct shrink_control *);
};
2.挂载描述符
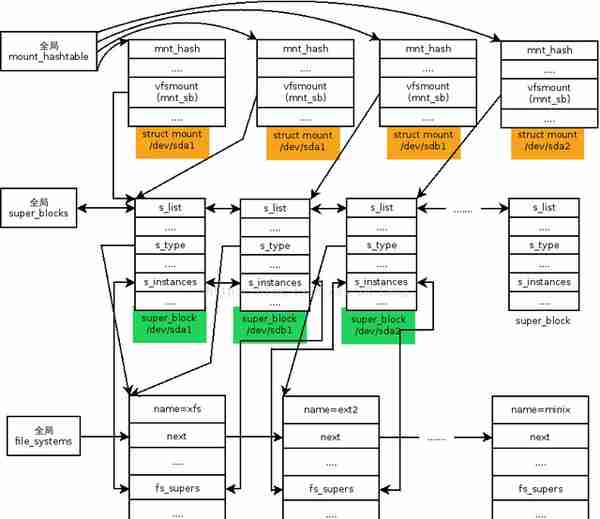
一个文件系统,只有挂载到内存中目录树的一个目录下,进程才能访问这个文件系统。每次挂载文件系统,虚拟文件系统就会创建一个挂载描述符。挂载描述符用来描述文件系统的一个挂载实例,同一个存储设备上的文件系统可以多次挂载,每次挂载到不同的目录下。结构体为struc mount,在fs/mount.h文件中:
struct mount {
struct hlist_node mnt_hash;//散列表
struct mount *mnt_parent;//父亲文件系统
struct dentry *mnt_mountpoint;//挂载点的目录
struct vfsmount mnt;//文件系统的挂载信息,结构体包含根目录和超级块
union {
struct rcu_head mnt_rcu;
struct llist_node mnt_llist;
};
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
struct mnt_pcp __percpu *mnt_pcp;
#else
int mnt_count;
int mnt_writers;
#endif
struct list_head mnt_mounts;//子文件系统链表头
struct list_head mnt_child;//父文件系统的mnt_mounts
struct list_head mnt_instance;//把挂载描述符添加到超级块的挂载实例链表中
const char *mnt_devname;//指向存储设备的名称,比如/dev/hda1
struct list_head mnt_list;
struct list_head mnt_expire; /* link in fs-specific expiry list */
struct list_head mnt_share;//共享挂载的循环链表
struct list_head mnt_slave_list;//从属挂载的链表
struct list_head mnt_slave;//用于从属挂载的链表
struct mount *mnt_master;//指向主挂载文件系统
struct mnt_namespace *mnt_ns;//指向挂载命名空间
struct mountpoint *mnt_mp;//指向挂载点
struct hlist_node mnt_mp_list;//把挂载描述符加入同一个挂载点的挂载描述符链表
struct list_head mnt_umounting; /* list entry for umount propagation */
#ifdef CONFIG_FSNOTIFY
struct fsnotify_mark_connector __rcu *mnt_fsnotify_marks;
__u32 mnt_fsnotify_mask;
#endif
int mnt_id;//挂载id
int mnt_group_id;挂载组id
int mnt_expiry_mark; /* true if marked for expiry */
struct hlist_head mnt_pins;
struct fs_pin mnt_umount;
struct dentry *mnt_ex_mountpoint;
} __randomize_layout;
3.文件系统类型
因为每种文件系统的超级块的格式不同,所以每种文件系统需要向虚拟文件系统注册文件系统类型 file_system_type,并且实现 mount 方法用来读取和解析超级块。结构体为struct file_system_type ,在include/linux/fs.h文件中:
struct file_system_type {
const char *name;//文件系统类型
int fs_flags;//使用标志
#define FS_REQUIRES_DEV 1 /* 文件系统在物理设备上 */
#define FS_BINARY_MOUNTDATA 2 /*二进制的数据结构数据,比如nfs */
#define FS_HAS_SUBTYPE 4 /* 文件系统含有子类型,比如fuse */
#define FS_USERNS_MOUNT 8 /* Can be mounted by userns root */
#define FS_RENAME_DOES_D_MOVE 32768 /* FS will handle d_move() during rename() internally. */
//挂载文件系统的回调函数,用来读取并且解析超级块
struct dentry *(*mount) (struct file_system_type *, int,
const char *, void *);
//卸载文件系统的回调函数
void (*kill_sb) (struct super_block *);
struct module *owner;//指向实现这个文件系统的模块,一般位THIS_MODULE
struct file_system_type * next;//指向文件系统链表下一种文件系统类型
struct hlist_head fs_supers;//该种类文件系统的超级块链表
struct lock_class_key s_lock_key;
struct lock_class_key s_umount_key;
struct lock_class_key s_vfs_rename_key;
struct lock_class_key s_writers_key[SB_FREEZE_LEVELS];
struct lock_class_key i_lock_key;
struct lock_class_key i_mutex_key;
struct lock_class_key i_mutex_dir_key;
};
4.索引节点
在文件系统中,每个文件对应一个索引节点,而且一个索引节点只有文件被访问才会在内存中创建。索引节点描述了两类数据信息,1.文件的属性,也称为元数据;2.文件数据的存储位置。当内核访问存储设备上一个文件的时候,会在内核中创建和初始化一个节点,结构体为struct inode,在include/linux/fs.h文件中:
struct inode {
umode_t i_mode;//文件的访问权限
unsigned short i_opflags;//
kuid_t i_uid;//使用者id
kgid_t i_gid;//使用组id
unsigned int i_flags;//文件系统标志
#ifdef CONFIG_FS_POSIX_ACL
//访问控制相关属性
struct posix_acl *i_acl;
struct posix_acl *i_default_acl;
#endif
const struct inode_operations *i_op;//索引节点操作方法函数
struct super_block *i_sb;//索引节点所属超级块
struct address_space *i_mapping;//相关地址映射(文件内容映射)
#ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY
void *i_security;//安全模块使用
#endif
/* Stat data, not accessed from path walking */
unsigned long i_ino;//索引节点号
/*
* Filesystems may only read i_nlink directly. They shall use the
* following functions for modification:
*
* (set|clear|inc|drop)_nlink
* inode_(inc|dec)_link_count
*/
union {
const unsigned int i_nlink;//硬链接计数
unsigned int __i_nlink;
};
dev_t i_rdev;//实际设备标识符
loff_t i_size;//文件长度
struct timespec64 i_atime;//最后访问时间
struct timespec64 i_mtime;//最后修改时间
struct timespec64 i_ctime;//最后改变时间
spinlock_t i_lock;//自旋锁
unsigned short i_bytes;//使用的字节数
u8 i_blkbits;//以位为单位的块大小
u8 i_write_hint;//
blkcnt_t i_blocks;//文件的块数
#ifdef __NEED_I_SIZE_ORDERED
seqcount_t i_size_seqcount;//对i_size进行串行计数
#endif
/* Misc */
unsigned long i_state;//索引状态标志
struct rw_semaphore i_rwsem;//读写信号量
unsigned long dirtied_when; /* jiffies of first dirtying */
unsigned long dirtied_time_when;//第一次弄脏数据时间
struct hlist_node i_hash;//散列表,用于快速查找
struct list_head i_io_list; /* backing dev IO list */
#ifdef CONFIG_CGROUP_WRITEBACK
struct bdi_writeback *i_wb; /* the associated cgroup wb */
/* foreign inode detection, see wbc_detach_inode() */
int i_wb_frn_winner;
u16 i_wb_frn_avg_time;
u16 i_wb_frn_history;
#endif
struct list_head i_lru;//最近最少使用链表
struct list_head i_sb_list;
struct list_head i_wb_list;//等待回写索引链表
union {
struct hlist_head i_dentry;//目录项链表
struct rcu_head i_rcu;//读拷贝链表
};
atomic64_t i_version;//版本号
atomic_t i_count;//引用计数
atomic_t i_dio_count;//直接io操作计数
atomic_t i_writecount;//写者计数
#ifdef CONFIG_IMA
atomic_t i_readcount;//读者计数
#endif
const struct file_operations *i_fop;//索引操作方法函数
struct file_lock_context *i_flctx;//
struct address_space i_data;//设备地址映射
struct list_head i_devices;//块设备链表
union {
struct pipe_inode_info *i_pipe;//管道信息
struct block_device *i_bdev;//块设备驱动
struct cdev *i_cdev;//字符设备驱动
char *i_link;//硬链接
unsigned i_dir_seq;//目录信号量
};
__u32 i_generation;
#ifdef CONFIG_FSNOTIFY
__u32 i_fsnotify_mask; /* all events this inode cares about */
struct fsnotify_mark_connector __rcu *i_fsnotify_marks;//文件系统通知掩码
#endif
#if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_FS_ENCRYPTION)
struct fscrypt_info *i_crypt_info;//加密信息
#endif
void *i_private; /* fs or device private pointer */
} __randomize_layout;
索引文件分为以下几种类型,在i_flags参数中区分:
内核支持两种链接:
索引节点的操作函数也很重要:
struct inode_operations {
//在特定目录中寻找索引节点
struct dentry * (*lookup) (struct inode *,struct dentry *, unsigned int);
const char * (*get_link) (struct dentry *, struct inode *, struct delayed_call *);//获取指定inode的连接
int (*permission) (struct inode *, int);//检查指定的inode是否允许访问
//获取访问控制方法函数
struct posix_acl * (*get_acl)(struct inode *, int);
int (*readlink) (struct dentry *, char __user *,int);
//创建一个索引节点,文件open时会用到
int (*create) (struct inode *,struct dentry *, umode_t, bool);
//创建硬链接,系统调用link会调用它
int (*link) (struct dentry *,struct inode *,struct dentry *);
//删除目录项指向的索引节点,系统调用unlink会调用它
int (*unlink) (struct inode *,struct dentry *);
//创建符号链接
int (*symlink) (struct inode *,struct dentry *,const char *);
int (*mkdir) (struct inode *,struct dentry *,umode_t);//创建目录
int (*rmdir) (struct inode *,struct dentry *);是//删除目录
int (*mknod) (struct inode *,struct dentry *,umode_t,dev_t);//创建特殊文件(设备文件,管道,套接字)
//移动文件
int (*rename) (struct inode *, struct dentry *,
struct inode *, struct dentry *, unsigned int);
int (*setattr) (struct dentry *, struct iattr *);//设置文件属性
int (*getattr) (const struct path *, struct kstat *, u32, unsigned int);//获取文件属性
ssize_t (*listxattr) (struct dentry *, char *, size_t);
//
int (*fiemap)(struct inode *, struct fiemap_extent_info *, u64 start,
u64 len);
int (*update_time)(struct inode *, struct timespec64 *, int);//更新访问时间
int (*atomic_open)(struct inode *, struct dentry *,
struct file *, unsigned open_flag,
umode_t create_mode);
int (*tmpfile) (struct inode *, struct dentry *, umode_t);
int (*set_acl)(struct inode *, struct posix_acl *, int);//设置访问控制参数
} ____cacheline_aligned;
5.目录项
目录项对象代表一个目录项,明明linux有个说法是一切皆文件,那为什么还要有目录项对象呢?因为虽然全部可以统一有索引节点表示,但是VFS需要经常执行目录相关操作,比如路径查找等,需要解析路径的每一个组成部分,不但要确保它有效,还需要进一步查找下一部分。解析一个路径并且遍历是一个耗时的,目录对象的引入会使得这个过程非常简单。目录项对象有struct dentry表示,在include/linux/dcache.h文件中:
struct dentry {
/* RCU lookup touched fields */
unsigned int d_flags;//目录项缓存标识符,由d_lock保护
seqcount_t d_seq;//目录项对象的顺序锁
struct hlist_bl_node d_hash;//散列表,方便查找
struct dentry *d_parent;//父目录的目录项对象
struct qstr d_name;//目录项名称
struct inode *d_inode;//该目录项下的索引节点
unsigned char d_iname[DNAME_INLINE_LEN];//存放短的文件名称
/* Ref lookup also touches following */
struct lockref d_lockref;//每个目录项的锁
const struct dentry_operations *d_op;//目录项操作方法函数
struct super_block *d_sb;//目录项所在的超级块
unsigned long d_time;//重置时间
void *d_fsdata;//文件系统特有数据
union {
struct list_head d_lru; //未使用链表的
wait_queue_head_t *d_wait;//等待队列
};
struct list_head d_child;//目录项下的子目录项链表
struct list_head d_subdirs;//目录项下所有目录项链表
/*
* d_alias and d_rcu can share memory
*/
union {
struct hlist_node d_alias;//索引节点别名链表
struct hlist_bl_node d_in_lookup_hash; /* only for in-lookup ones */
struct rcu_head d_rcu;//rcu加锁
} d_u;
} __randomize_layout;
和前面两个对象不同,目录项对象没有对应的磁盘结构,VFS根据字符串形式的路径现场创建它,由于目录项对象没有真正的保存在磁盘中,目录项没有修改标志、回写等。目录项有三种状态:
如果VFS遍历路径名中的所有元素并解析成目录项对象,还要达到最深层次,这是非常费力的事情,会浪费大量时间,所以VFS会对目录项对象遍历解析,解析完毕后会缓存在dcache中,缓存主要包括三部分:
现在看看目录项的操作函数:
struct dentry_operations {
//判断目录项对象是否有效
int (*d_revalidate)(struct dentry *, unsigned int);
int (*d_weak_revalidate)(struct dentry *, unsigned int);
//目录项对象生产散列值,加入散列表是需要此函数
int (*d_hash)(const struct dentry *, struct qstr *);
//文件名对比,根据文件系统类型定制,因为有些文件系统不区分大小写
int (*d_compare)(const struct dentry *,
unsigned int, const char *, const struct qstr *);
//删除目录项对象,当d_count为0时调用
int (*d_delete)(const struct dentry *);
//创建和初始化目录项对象
int (*d_init)(struct dentry *);
//释放目录项对象,默认情况下什么都不做
void (*d_release)(struct dentry *);
void (*d_prune)(struct dentry *);
//释放索引节点,当磁盘索引被删除时调用
void (*d_iput)(struct dentry *, struct inode *);
char *(*d_dname)(struct dentry *, char *, int);
struct vfsmount *(*d_automount)(struct path *);
int (*d_manage)(const struct path *, bool);
struct dentry *(*d_real)(struct dentry *, const struct inode *);
} ____cacheline_aligned;
6.文件对象
文件对象代表进程打开的文件,包括普通文件和目录文件,是用户直接操作的对象,也是用户最熟悉的对象。他是由open创建,close撤销使用的。通过文件对象,VFS可以找到其对应的目录项和索引节点,从而找到所在的超级块。文件对象实际上没有对应的磁盘结构,他的作用是连接用户和VFS,给与用户操作文件的方法,从而实现间接操作磁盘文件。文件对象由struct file结构体表示,在在include/linux/fs.h文件中:
struct file {
union {
struct llist_node fu_llist;//文件对象链表
struct rcu_head fu_rcuhead;//释放后的rcu链表
} f_u;
struct path f_path;//包含文件目录项
struct inode *f_inode;//文件对应的索引节点
const struct file_operations *f_op;//文件的操作方法函数
/*
* Protects f_ep_links, f_flags.
* Must not be taken from IRQ context.
*/
spinlock_t f_lock;//单个文件锁
enum rw_hint f_write_hint;//文件的写生命时间
atomic_long_t f_count;//文件对象使用计数
unsigned int f_flags;//当打开文件时指定的标志
fmode_t f_mode;//文件的访问模式,比如读、写、创建
struct mutex f_pos_lock;//f_pos的互斥锁
loff_t f_pos;//文件的当前位移量
struct fown_struct f_owner;//拥有者通过信号进行异步IO数据传送
const struct cred *f_cred;//文件的信任状
struct file_ra_state f_ra;//预读状态信息
u64 f_version;//版本号
#ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY
void *f_security;//安全模块
#endif
/* needed for tty driver, and maybe others */
void *private_data;//私有数据,一般用于指向tty驱动
#ifdef CONFIG_EPOLL
/* Used by fs/eventpoll.c to link all the hooks to this file */
struct list_head f_ep_links;//事件池链表
struct list_head f_tfile_llink;//所有文件的事件池链表
#endif /* #ifdef CONFIG_EPOLL */
struct address_space *f_mapping;//文件页缓存映射
errseq_t f_wb_err;//文件回写错误状态标志位
} __randomize_layout
文件对象的操作方法函数很重要,由struct file_operations表示:
struct file_operations {
struct module *owner;
//更新文件的位置偏移量,由系统调用llseek调用它
loff_t (*llseek) (struct file *, loff_t, int);
ssize_t (*read) (struct file *, char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);//读
ssize_t (*write) (struct file *, const char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);//写
//同步读写函数,有对应的系统调用函数调用他们
ssize_t (*read_iter) (struct kiocb *, struct iov_iter *);//同步读
ssize_t (*write_iter) (struct kiocb *, struct iov_iter *);//同步写
int (*iterate) (struct file *, struct dir_context *);
int (*iterate_shared) (struct file *, struct dir_context *);
//函数睡眠等待给定的文件活动,由系统调用poll调用
__poll_t (*poll) (struct file *, struct poll_table_struct *);
//给设备文件发送命令参数,有系统调用ioctl调用
long (*unlocked_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
long (*compat_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
//文件映射到应用层
int (*mmap) (struct file *, struct vm_area_struct *);
unsigned long mmap_supported_flags;
int (*open) (struct inode *, struct file *);//打开
int (*flush) (struct file *, fl_owner_t id);//刷新
int (*release) (struct inode *, struct file *);//关闭
int (*fsync) (struct file *, loff_t, loff_t, int datasync);//回写到硬盘
int (*fasync) (int, struct file *, int);//同步回写到硬盘
int (*lock) (struct file *, int, struct file_lock *);//给文件上锁
ssize_t (*sendpage) (struct file *, struct page *, int, size_t, loff_t *, int);
//获取未使用的内存映射文件
unsigned long (*get_unmapped_area)(struct file *, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long);
int (*check_flags)(int);//检查flags的有效性,一般用于nfs,它不允许O_APPEND和O_DIRECT结合
//忠告锁,由系统调用flock调用它
int (*flock) (struct file *, int, struct file_lock *);
ssize_t (*splice_write)(struct pipe_inode_info *, struct file *, loff_t *, size_t, unsigned int);
ssize_t (*splice_read)(struct file *, loff_t *, struct pipe_inode_info *, size_t, unsigned int);
int (*setlease)(struct file *, long, struct file_lock **, void **);
long (*fallocate)(struct file *file, int mode, loff_t offset,
loff_t len);
void (*show_fdinfo)(struct seq_file *m, struct file *f);
#ifndef CONFIG_MMU
unsigned (*mmap_capabilities)(struct file *);
#endif
ssize_t (*copy_file_range)(struct file *, loff_t, struct file *,
loff_t, size_t, unsigned int);
int (*clone_file_range)(struct file *, loff_t, struct file *, loff_t,
u64);
int (*dedupe_file_range)(struct file *, loff_t, struct file *, loff_t,
u64);
int (*fadvise)(struct file *, loff_t, loff_t, int);
} __randomize_layout;
总结:
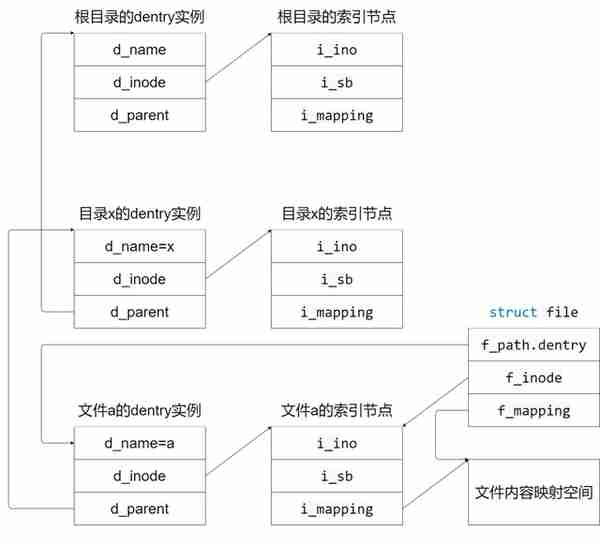
我们在进程中挂载了一个文件系统,也就是说找到了这个超级块super_block结构体,可以通过super_block结构体中的s_inodes(索引)找到对应的文件,同时,在遍历inodes的时候,会自动的解析inode路径的每一个组成部分,组成struct dentry(目录项),方便系统使用树的形式表示inode(索引)之间的关系。这样子我们打开了这个磁盘挂载的目录就可以看到磁盘的目录和文件了,我们打开了一个索引,系统会创建一个struct file(文件)结构体,这就是我们平时操作一个文件的方式了。
相反,我们在进程中操作一个文件(struct file),可以通过struct file中的struct inode参数找到其索引,进而找到超级块(struct super_block),这样子,VFS就知道要操作的文件系统和索引了。
上面的是VFS对上层的通道,对底层又会是怎么样子呢?其实,在内核初始化的时候,会注册了一种文件系统类型,VFS挂载这种文件系统会根据super_block结构体中struct file_system_type *s_type,找到这个文件系统类型,内核才可以根据文件系统类型来调用对应超级块的操作函数,因为每一种文件系统类型的超级块操作函数具体是实现是不同的。然后在挂载这种文件系统的时候,会创建一个struct mount 实例,当然,比如有两个u盘,要挂载两个,就要有两个struct mount 实例。
补充一下,file_system_type、 super block、 mount的关系图:
file 、dentry 、inode 关系图:
下一期具体讲一下VFS对底层的交互吧。
推荐阅读

-
邮政信用卡管理中心电话(邮政信用卡管理中心电话是多少)
2023-04-28
索引文件分为以下几种类型,在i_flags参数中区分:内核支持两种链接:索引节点的操作函数也很重要:struct ino...
-
铁矿石期货炒单(铁矿石期货交易手册)
2023-04-28
索引文件分为以下几种类型,在i_flags参数中区分:内核支持两种链接:索引节点的操作函数也很重要:struct ino...

-
深圳社保新规挂靠
2023-04-28
索引文件分为以下几种类型,在i_flags参数中区分:内核支持两种链接:索引节点的操作函数也很重要:struct ino...

-
沈阳的房地产评估有限公司(沈阳市房地产估价师协会网站)
2023-04-28
索引文件分为以下几种类型,在i_flags参数中区分:内核支持两种链接:索引节点的操作函数也很重要:struct ino...
-
淄博新联化物流有限公司(新联化工有限公司)
2023-04-28
索引文件分为以下几种类型,在i_flags参数中区分:内核支持两种链接:索引节点的操作函数也很重要:struct ino...
-
股票dma的牛公式(股票dma指标详解)
2023-04-28
索引文件分为以下几种类型,在i_flags参数中区分:内核支持两种链接:索引节点的操作函数也很重要:struct ino...